Today marks 240 days since an event the Ethereum community has come to know as “the merge.” And its effects on the total ETH supply are clear.
Arguably the most significant upgrade in its history, the merge saw the Ethereum network transition from a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to one based on Proof of Stake (PoS). Now, eight months on from the pivotal event, the long-term consequences of the merge are becoming apparent.
ETH Supply Declines
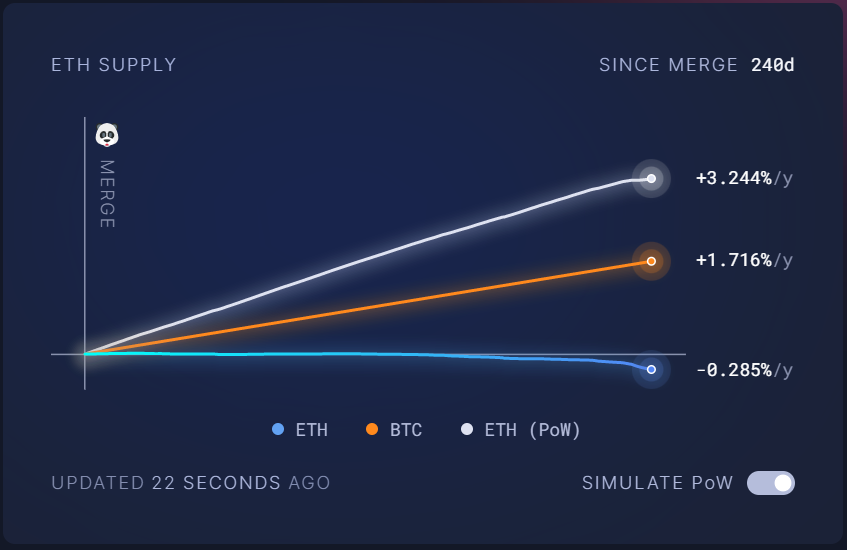
According to the Ethereum analytics dashboard ultrasound.money, nearly 650,000 ETH has been burned since the merge. In the same time span, just under 424,000 new ETH have been minted. The result is a net supply change of around -226,000 ETH.
As a percentage of the total supply, the numbers represent a decrease of 0.213% or 0.285% annualized.
Had the merge not happened, ultrasound.money estimates that the total ETH supply would have increased at a rate of 3.244% per year in the same period.
Long-term Ether holders will likely welcome the news. After years of increasing supply, the higher burn rate in the past 240 days represents a deflationary trajectory. This could reward investors by pushing the price of ETH up.
Driving Ethereum’s post-merge supply dynamics is a technical change that saw the network replace miners with validators. Crucially, validator rewards are significantly less than the mining rewards issued under the PoW system.
This is because operating a validating node is n
Go to Source to See Full Article
Author: James Morales






